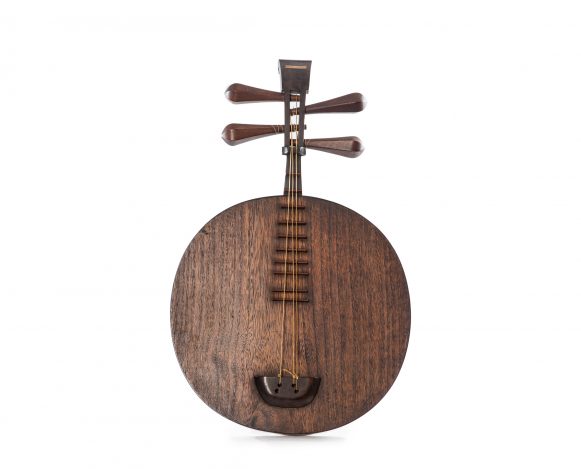
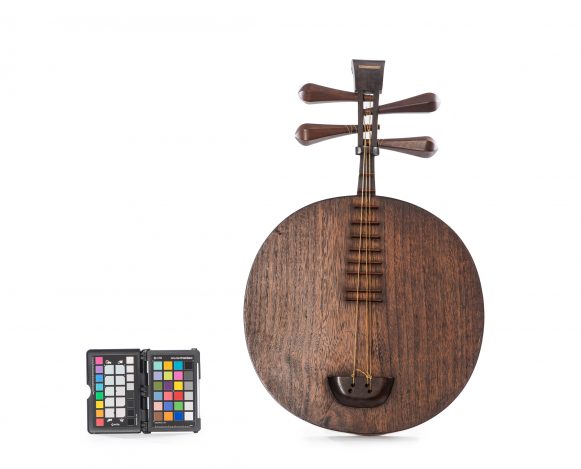
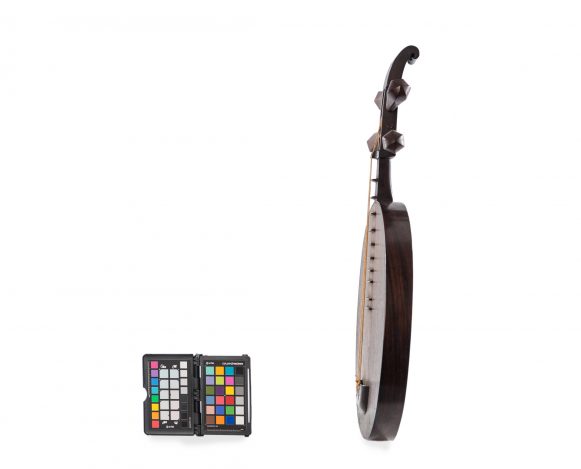
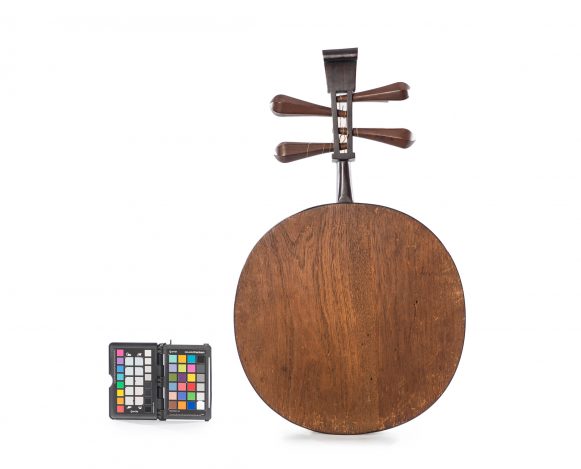
The Yueqin is a traditional instrument from China. The term literally means ‘moon qin’, which is popularly translated into the English language as moon lute. The instrument can be considered an offspring of the old ruan, a lute described with different names in the literature about the Han Dinasty (206 B.C- 220 A.D). During the Tang Dinasty (618-907), the instrument was commonly known as ruanxian (Xian was the name of the famous musician of the 3rd century). On the Yueshu music treaty (written around 1100 A.D.), the ruanxin is described as having a round shape resonance box, long neck, four strings and thirteen frets, but it is more often called as yueqin than ruanxian. The works of art from this period show various ruanxian in different instruments ensembles, which proves the instrument’s popularity. However, the use of the Yueqin has fallen with time and it has survived marginally until the 20th century. When the modern ensembles from concert rooms were formed during the second half of the 20th century, the ruanxian (popularly known as Ruan) got back to being used, and along with the yueqin they have been modified by the government instrument factories: frets were added (up to twenty four) to increase the reach and the chromatic capacity, and those were repositioned so that the instrument would fit the Western ideal of an equal temperament. The Yueqin’s size was maintained, but the number of strings was shortened from four to three, and those are tuned in distant pitches so that the instruments can reach a wider extension. Despite these changes, the new yueqin was not widely accepted in modern Chinese orchestras, being most frequently used in Beijing Opera ensembles. Yueqin variations are also used for accompanying dancing songs and in other minority peoples from the Southwest of China. Previous inventories from the museum inform that this specimen had four silk strings, which indicates that it is a traditional Yueqin. In traditional instruments, four silk strings are gathered in two sets of strings and tuned in fifths.